Your sales team closes a deal. Marketing celebrates a campaign win. Your product team ships a new feature. But here’s the problem: none of them are talking about the same customer. Sales chases enterprise logos. Marketing targets mid-market. Product builds for startups. The result? Wasted budget, missed quotas and a customer experience that feels disjointed at every touchpoint.
This isn’t just inefficiency. It’s a cycle of wasted resources and missed revenue. Every dollar spent attracting the wrong audience is a dollar you can’t use to delight your perfect customer. Every hour your sales team spends on dead-end leads is an hour they could spend closing deals that matter.
The solution is a data-driven customer profile. It’s your map to finding, attracting and retaining your most profitable customers. This guide provides the step-by-step process, expert examples and a free template to build profiles that become the foundation for scalable growth.
In this piece, we’ll show you how to create a customer profile by covering the following sections:
- What a customer profile is and how it differs from an ICP and buyer persona
- Why customer profiles are non-negotiable for growth
- The primary types of customer profiling methods
- A 5-step process to create your customer profile
- How to activate your profiles across marketing, sales and product
- Examples and a free downloadable template
- The best customer profiling software and tools
Let’s get started.
What Is a Customer Profile?
A customer profile is a factual description of a target audience segment based on collected data. It outlines the shared characteristics of a group of customers, including demographics (age, gender, income, education), geographic location (country, region, city), firmographics for B2B (company size, industry, revenue), behavioral patterns (purchasing habits, product usage) and psychographics (interests, values, lifestyle).
These profiles help your teams build and share clearer pictures of your ideal customers. They transform abstract market segments into concrete, actionable descriptions that guide decision-making across your business.
Building an accurate customer profile is a repeatable process driven by data. It requires collecting information from multiple sources, analyzing patterns and continuously refining your understanding as your market evolves.
What Is the Difference Between a Customer Profile, an Ideal Customer Profile and a Buyer Persona?
The difference between a customer profile, an Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) and a buyer persona is that each serves a distinct strategic purpose in your go-to-market strategy.
A customer profile is a broad, factual description of a target audience segment. It outlines the shared characteristics of a group of customers based on collected data. Customer profiles help you understand your market segments at a high level and inform strategic decisions about which audiences to target.
An Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) is a detailed, data-driven description of a fictional company that would gain the most value from your product or service and provide the most value to your business. It is used in B2B contexts to identify the most valuable types of companies to target. The ICP focuses on firmographics such as industry, company size, revenue, technology stack and funding stage to define the perfect organizational fit.
A buyer persona is a semi-fictional, in-depth representation of an individual within your ICP. It humanizes a customer segment by giving them a name, a job title, goals, motivations and pain points. While an ICP tells you which companies to target, a buyer persona tells you who to talk to within those companies and how to talk to them.
Here’s a comparison table to clarify the differences:
| Aspect | Customer Profile | Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) | Buyer Persona |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Broad customer segment | Perfect company/account | Individual decision-maker |
| Primary Use | Market segmentation | Strategic targeting and qualification | Content and messaging personalization |
| Key Data | Demographics, behaviors, geographics | Firmographics, technographics, budget | Psychographics, goals, challenges, objections |
| Best For | Understanding market segments | B2B account-based marketing and sales | Crafting targeted messaging and content |
| Example | “Small business owners in the US” | “Series B SaaS companies with 50-200 employees” | “Sarah, VP of Marketing at a growth-stage startup” |
In practice, these three tools work together. Your customer profile helps you identify broad market segments. Your ICP narrows that down to the specific types of companies you should prioritize. Your buyer personas guide how you communicate with the individuals within those companies.

Why Are Customer Profiles Important for Growth?
Customer profiles are important for growth because they transform guesswork into data-driven strategy. According to McKinsey & Company research from 2023, personalization can lift revenues by 5 to 15 percent, increase marketing ROI by 10 to 30 percent and reduce customer acquisition costs by as much as 50 percent. Their findings also show that 71% of consumers expect personalized interactions and 76% get frustrated when this does not happen. Companies that excel at personalization generate 40% more revenue from these activities than average players.
Salesforce’s 8th Edition ‘State of the Connected Customer’ report, which surveyed 14,300 consumers and 3,300 business buyers across 25 countries, found that 80% of customers now believe the experience a company provides is as important as its products or services.
Here are the key ways customer profiles benefit your business:
Lower Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
Customer profiles lower customer acquisition costs because they help you stop wasting budget on audiences that will never convert. When you know who your best customers are, your marketing team can configure campaigns to reach the right people on the right channels with the right message. This precision reduces wasted ad spend and improves conversion rates across every stage of your funnel.
Increase Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)
Customer profiles increase customer lifetime value because they help you identify the characteristics of customers who stay longer and spend more. By focusing your acquisition efforts on prospects who match these patterns, you improve retention and increase lifetime value. You’re not just finding customers; you’re finding the right customers.
Enable Personalization at Scale
Customer profiles enable personalization at scale because they allow your teams to deliver personalized experiences without manual effort. Marketing automation platforms can segment audiences automatically. Sales teams can tailor their outreach based on prospect characteristics. Support teams can anticipate needs before customers ask.
Inform Product Development
Customer profiles inform product development because they reveal what your best customers need, how they use your product and where they experience friction. This insight helps your product team prioritize features that drive the most value for the customers who matter most. You stop building for everyone and start building for the people who will love what you create.
What Are the Primary Types of Customer Profiling?
The primary types of customer profiling are demographic, geographic, psychographic, behavioral, firmographic and technographic profiling. Each method answers different strategic questions about your customers and provides distinct insights that guide your marketing, sales and product decisions.
What Is Demographic Profiling?
Demographic profiling is the segmentation of customers based on quantifiable personal attributes like age, gender, income, education level, marital status and occupation. This is the most common form of customer segmentation and provides a foundation for understanding your market.
For example, a B2C e-commerce brand might discover that their highest-value customers are women aged 25-40 with household incomes above $75,000.
What Is Geographic Profiling?
Geographic profiling is the segmentation of customers based on their physical location, from a broad country level down to a specific neighborhood or ZIP code. This is valuable for businesses with regional variations in demand, pricing or distribution.
For example, a retail chain might find that their urban stores perform better with certain product categories while suburban locations favor different inventory.
What Is Psychographic Profiling?
Psychographic profiling is the grouping of customers based on psychological attributes like personality, values, interests, lifestyle, attitudes and beliefs. It moves beyond who the customer is to why they buy and is considered the study of Activities, Interests and Opinions (AIOs).
For instance, two customers might have identical demographics but different psychographics. One values sustainability and ethical sourcing, while the other prioritizes convenience and price. Understanding these differences allows you to craft messaging that resonates with each segment.
What Is Behavioral Profiling?
Behavioral profiling is the analysis of customers’ actions and interactions with your company. It includes purchasing history, product usage frequency, brand loyalty, website interactions and response to marketing campaigns. Behavioral data reveals patterns that predict future actions.
For example, you might identify a segment of customers who purchase every 90 days, always during promotional periods and through mobile devices. This insight allows you to optimize your promotional calendar and mobile experience to serve this segment better.
What Is Firmographic Profiling?
Firmographic profiling is the B2B equivalent of demographic profiling. It segments organizations based on their attributes, such as industry, company size, location, revenue, legal structure and funding stage. This helps B2B companies identify which types of organizations are the best fit for their solution.
For example, a B2B marketing automation platform might define their ICP as Series B SaaS companies with 50-200 employees and $10-50M in annual revenue.
What Is Technographic Profiling?
Technographic profiling is the segmentation of companies based on the technologies they use, including their software stack, hardware infrastructure and digital tools. This is valuable for B2B SaaS companies that need to understand whether their solution integrates with a prospect’s existing tech stack.
For example, a sales enablement platform might target companies currently using Salesforce as their CRM and actively hiring sales roles.

How Can You Create a Customer Profile in 5 Steps?
You can create a customer profile in 5 steps by gathering data, identifying your best customers, finding patterns, drafting your profile and refining it. This process transforms raw data into strategic insight that drives growth across your organization.
How Do You Gather Customer Data?
You gather customer data by collecting quantitative and qualitative information from multiple sources. You need both types of data to build a complete picture of your customers.
Internal data (first-party data) comes from systems you already own:
- CRM systems containing demographic and contact information
- Transactional data including purchase history and payment methods
- Website and app analytics tracking user behavior
- Support interactions revealing pain points
- Email marketing engagement metrics
Direct customer feedback (zero-party data) comes from asking customers:
- Surveys and questionnaires asking about needs and preferences
- Interviews and focus groups for qualitative insights
- Website forms and preference centers
- Interactive campaigns like contests
When creating surveys, use Likert scales (rating scales with 5 or 7 points that measure the intensity of a respondent’s opinion) to quantify subjective feedback. For interviews, use the ‘5 Whys’ technique to uncover root motivations by asking ‘why’ repeatedly to drill down to core issues.
External and third-party data fills gaps in your knowledge:
- Third-party data enrichment to append demographic and firmographic details
- Social media insights for sentiment analysis
- Industry reports for market context
- Second-party data from trusted partners
For B2B companies, platforms like UpLead provide access to over 155 million business contacts with verified email addresses, phone numbers and firmographic data. This allows you to enrich your existing customer records and fill in missing information about company size, industry, revenue and technology stack.
How Do You Identify Your Best Customers?
You identify your best customers through analysis of revenue, retention and cost data. Your best customers are those who generate the most revenue, stay the longest, refer others and cost the least to serve.
Use RFM (Recency, Frequency, Monetary) Analysis to identify your most valuable customers:
- Score each customer on a scale of 1-5 for how recently they purchased
- Score each customer on how often they purchase
- Score each customer on how much they spend
- Group customers based on their combined scores
For example, a ‘555’ score represents ‘Best Customers’ (very recent, frequent, high-spending), while a ‘155’ score represents ‘At-Risk Champions’ (spent a lot and frequently but haven’t purchased in a long time). Klaviyo is an AI-powered email and SMS marketing platform that offers built-in RFM analysis tools, automatically analyzing customer purchase behavior to assign scores and segment audiences into distinct groups such as ‘Champions’, ‘Loyal’, ‘At risk’ and ‘Inactive’ customers.
Also perform Cohort Analysis by grouping users based on shared characteristics (such as acquisition date) and tracking them over time to understand behavior, engagement and retention. Mixpanel is a product analytics service that enables the creation of user cohorts based on shared behaviors and attributes to track engagement and retention over time.
How Do You Find Patterns in Customer Data?
You find patterns in customer data by analyzing commonalities among your best customers. Once you’ve identified your most valuable customer segment, analyze what they have in common.
Collate all of your data in one place and sort through it systematically. Look for patterns across demographic attributes (age, gender, income, education), geographic location (country, region, city), firmographic data for B2B (industry, company size, revenue), behavioral patterns (purchasing frequency, product usage, engagement), psychographic traits (values, interests, pain points) and technographic data (technology stack, tools used).
For instance, you might discover that your best B2B customers are all Series B SaaS companies with 50-200 employees, using Salesforce as their CRM and expanding their marketing teams. Or for B2C, you might find that your highest lifetime value customers are women aged 30-45, living in urban areas, who value sustainability and make their first purchase during seasonal promotions.
How Do You Draft a Customer Profile?
You draft a customer profile by documenting identified patterns in a structured template. Now that you’ve identified patterns, it’s time to document them in a format that your teams can use.
A comprehensive customer profile template should include:
For B2B profiles:
- Firmographics (industry, company size, revenue, annual budget)
- Technographics (technology stack, tools used)
- Buying process and committee (decision-making structure, stakeholder roles)
- Pain points and goals (business-level challenges)
- Behavioral and operational needs
For B2C profiles:
- Demographics (age, gender, income, education)
- Psychographics (lifestyle, values, interests)
- Behavioral patterns (buying habits, brand loyalty)
- Pain points and goals (personal challenges)
- Information sources (where they research and discover products)
Create your first draft and share it with stakeholders across sales, marketing and product teams. Collect their feedback to ensure the profile reflects reality and will be useful in practice. This collaborative approach ensures buy-in and catches blind spots.
How Do You Refine Customer Profiles Over Time?
You refine customer profiles over time by using, validating and updating them based on real-world results. Customer profiles are not static documents. They must evolve as your market, product and business strategy change.
Outline a trial period for your customer profile. For instance, your teams could use your customer profile for one month and assess whether it works. At the end of the trial period, collect feedback from all key stakeholders and revise your profile based on real-world use.
To maintain your customer profiles over time, schedule a regular time to review and revise them, incorporate new insights from your sales team after every quarter, use your marketing analytics to monitor changes constantly and update profiles whenever there are significant market, product or business strategy shifts.
For dynamic sectors like e-commerce or subscription services, monthly or quarterly updates are recommended. For B2B companies, a semi-annual or annual review is often sufficient. At minimum, profiles should be reviewed at least once a year.

How Can You Use Customer Profiles in Marketing?
You can use customer profiles in marketing by segmenting audiences for targeted campaigns, creating content addressing specific pain points, optimizing communication channels and building lookalike audiences for advertising platforms.
For example, if your customer profile reveals that your best customers discover you through LinkedIn and value detailed case studies, you can allocate more budget to LinkedIn advertising and produce more case study content. If your profile shows that customers prefer email communication over phone calls, you can adjust your outreach strategy accordingly.
How Can You Use Customer Profiles in Sales?
You can use customer profiles in sales by prioritizing leads based on ICP matching, personalizing outreach with prospect insights, preparing for objection handling and focusing time on the highest-value opportunities.
Prospecting tools like UpLead allow sales teams to find new prospects matching their ideal customer profile by filtering a database of over 155 million contacts by job title, industry, location, company size and technologies used. This ensures that every outreach effort targets prospects who closely match your best customers.
For instance, if your customer profile indicates that your best customers are VP-level marketing leaders at Series B SaaS companies using Salesforce, you can use these exact filters to build a targeted prospect list and craft personalized messaging that speaks to their challenges.
How Can You Use Customer Profiles in Product Development?
You can use customer profiles in product development by prioritizing features based on customer feedback and usage data, informing the long-term product roadmap with market needs and enhancing user experience by identifying friction points.
When your product team understands who your best customers are and what they need, they can make better decisions about which features to build next. Instead of trying to serve everyone, they can focus on delivering value to the customers who matter most to your business.
What Are Examples of Customer Profiles?
Examples of customer profiles range from simple one-page summaries to detailed multi-section documents. The best customer profiles share a common trait: they provide actionable information that guides strategic decisions across your organization.
Five Abilities – Rick Wong
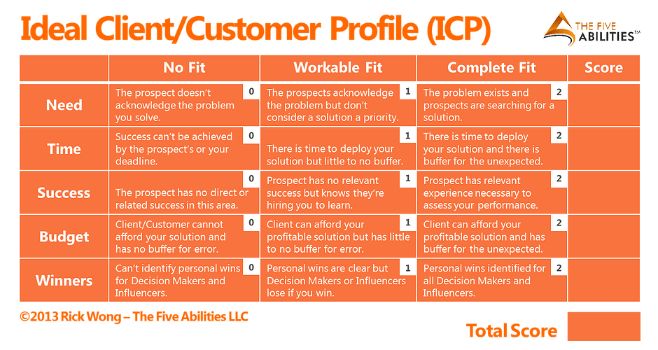
This example from Rick Wong shows a scoring system to assess whether a prospect is viable. This system uses five key criteria to evaluate each prospect or group. Each criterion has three possible outcomes with an assigned score. You go through each section and attribute a score to your customer in each category. By the end, you arrive at a final score that you can use to rank and sort your customers.
For instance, you might decide that any customer with a score above six is considered ideal. This system gives you a fast, rough way to sort through a high volume of prospects.
Infrastructure Group LLC – Ideal Customer Breakdown
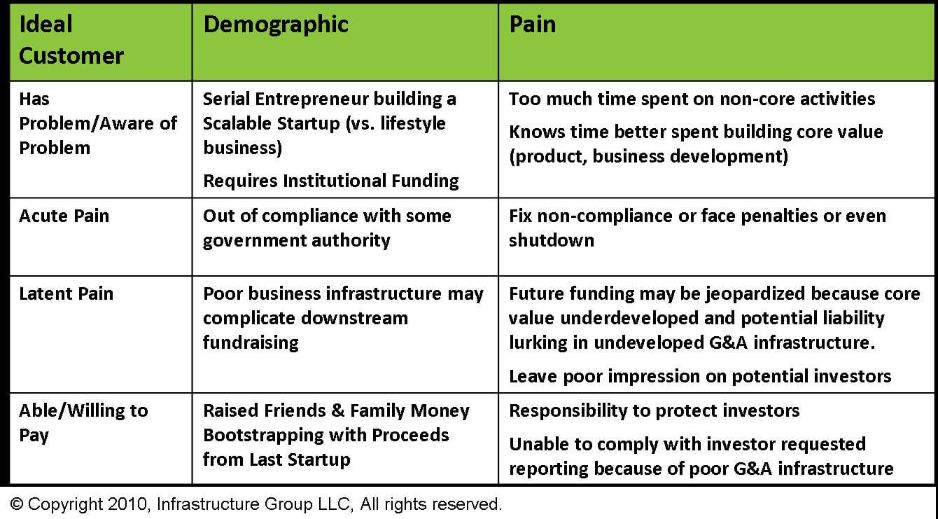
This example breaks down customers according to the severity of their pain points. Each group is further broken down into demographic groups to help teams within your business paint a clearer mental picture.
This example places a strong emphasis on understanding the pain points and perspectives of customers. This illustrates how important it is to understand that your customers have particular frustrations or pain points and whether you can serve them.
ringDNA – Buyer Personas

This customer profile example from ringDNA shows a more traditional buyer persona. This business has provided a helpful image to help salespeople visualize who they’re targeting.
This profile also has a host of useful demographic and firmographic information. It paints a more complete image and answers key questions your team members might have about their prospects and customers.
Since this example focuses on tools and applications, it is helpful for SaaS sales. This feature helps these businesses gauge whether their solution will fit alongside the customer’s existing tech stack.
Where Can You Find a Free Customer Profile Template?
You can find a free customer profile template from several sources. Several free customer profile templates are available to help you get started.
Demand Metric offers an active downloadable Excel template that requires user information for access. This template provides a structured format for documenting customer characteristics and is suitable for both B2B and B2C businesses.
Fit Small Business actively offers free customer profile and customer persona templates in PDF and Word formats from March 2024. These templates provide comprehensive sections for demographics, psychographics and behavioral information.
When selecting a template, choose one that matches your business model (B2B or B2C) and includes fields for all the customer profiling types relevant to your strategy. The template should be easy to fill out, share with your team and update as your understanding evolves.
What Are the Best Tools for Collecting Customer Data?
The best tools for collecting customer data are SurveyMonkey, Typeform and UXtweak. These platforms make it easy to gather quantitative and qualitative feedback from customers at scale.
SurveyMonkey is an online survey platform with AI-powered survey creation, over 500 templates, 25+ question types and tools for distributing surveys via email, web links, social media and QR codes. This platform makes it easy to collect quantitative feedback from customers at scale.
Typeform is a SaaS company specializing in interactive online forms and surveys with a conversational ‘one question at a time’ interface, Logic Jumps and integration with over 300 third-party applications. Typeform is effective for improving survey completion rates through its engaging user experience.
UXtweak is an all-in-one UX research platform offering Website and Mobile App Testing, Session Recording, Surveys, Card Sorting, Tree Testing and Prototype Testing. This tool helps you understand how customers interact with your product and where they experience friction.
What Are the Best Tools for Analyzing Customer Data?
The best tools for analyzing customer data are HubSpot, Google Analytics 4 and Mixpanel. These platforms provide robust reporting capabilities that make it easy to gain insights from your customer data.
HubSpot is a comprehensive customer platform with an AI-powered Smart CRM and free ‘Make My Persona’ tool for creating detailed customer profiles. HubSpot’s CRM provides robust reporting capabilities that make it easy to gain insights from your customer data.
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is the current standard for web analytics, using an event-based measurement model to provide AI-powered insights and track user behavior across websites and apps. GA4 helps you understand how customers interact with your digital properties and identify patterns in their behavior.
Mixpanel is a product analytics service that enables the creation of user cohorts based on shared behaviors and attributes to track engagement and retention over time. This is valuable for SaaS companies that need to understand how different customer segments use their product.
What Are the Best Tools for Enriching Customer Data?
The best tool for enriching customer data is UpLead. This platform helps businesses enrich their existing customer records and find new prospects that match their ideal customer profile.
UpLead is a B2B data provider with real-time verified contact and company data, over 50 search filters and access to more than 155 million business contacts with 95% data accuracy. UpLead helps businesses enrich their existing customer records and find new prospects that match their ideal customer profile by filtering by job title, industry, location, company size and technologies used.
For example, if your customer profile reveals that your best customers are VP-level marketing leaders at Series B SaaS companies using Salesforce, you can use UpLead’s filters to build a targeted prospect list and export verified contact information to your CRM.
What Are the Best Tools for Creating Customer Profiles?
The best tools for creating customer profiles are Miro and HubSpot’s Make My Persona. These platforms make it easy for teams to collaborate on building and refining customer profiles.
Miro is an online visual collaboration platform with an ‘infinite canvas’, offering over 5,000 templates and real-time collaboration features ideal for creating user personas and customer journey maps. Miro makes it easy for teams to collaborate on building and refining customer profiles.
HubSpot’s Make My Persona tool allows businesses to create professional, customizable customer profiles via an intuitive generator. If you’re looking for a simple way to assemble your customer profiles, this free tool is a great choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should customer profiles be updated?
Customer profiles should be treated as living documents. For dynamic sectors like e-commerce or subscription services, monthly or quarterly updates are recommended. For B2B companies, a semi-annual or annual review is often sufficient. Profiles should be reviewed at least once a year and whenever there are significant market, product or business strategy shifts.
What is the difference between a customer profile and market segmentation?
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad target market into smaller, distinct groups based on shared characteristics. A customer profile is a much more detailed, semi-fictional depiction of an ideal individual or company within a segment. Segmentation tells you where to aim, while profiles tell you how to connect and resonate on a human level.
How do data privacy laws like GDPR affect customer profiling?
Under GDPR, businesses must inform individuals that their data is being used for profiling and explain the logic and consequences. Individuals have the right to object to profiling for direct marketing. Under CCPA/CPRA, consumers have the right to know what personal data is collected, the right to have it deleted and the right to opt-out of the sale or sharing of their data. Always ensure your data collection and profiling practices comply with applicable privacy regulations.
Can you have more than one customer profile?
Most experts recommend starting with a single, clearly defined Ideal Customer Profile. For most small to medium-sized businesses, creating 3 to 5 distinct profiles is sufficient to cover primary customer segments without diluting the marketing message. Having too many profiles can lead to confusion and diluted focus across your teams.
Build Your Foundation for Growth
We hope this guide helps you master customer profiles. These tools can transform your business when used correctly. They turn abstract market segments into concrete, actionable descriptions that guide decision-making across marketing, sales and product.
After you’ve put together great customer profiles, you’ll need to put them to use and seek out your ideal customers. To access high-quality lead information and make the most of your customer profiles, start your free UpLead trial today.